GUM-HEALTH
Periodontitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
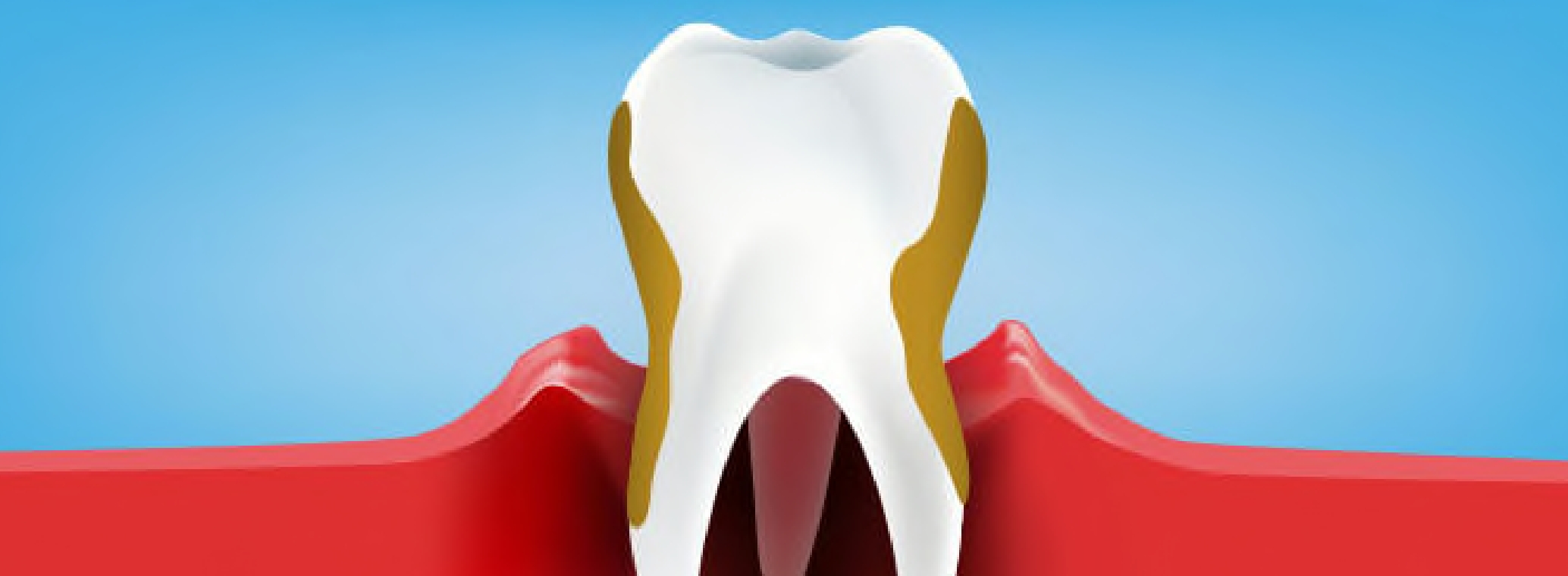 What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis Symptoms and Causes
Periodontitis Treatment
Prevent Periodontitis: Stop Gingivitis Before It Starts
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis Symptoms and Causes
Periodontitis Treatment
Prevent Periodontitis: Stop Gingivitis Before It Starts
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis refers to advanced periodontal disease. With periodontitis, the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, creating pockets where additional bacteria can build up and cause an infection. Treatment of advanced periodontal disease is a multi-step process. Sometimes a periodontist will recommend medications as a first-line treatment for advanced periodontal disease before resorting to surgery, depending on the severity of your gum disease.
Periodontitis Symptoms and Causes
Whereas gingivitis symptoms such as sore gums and bleeding gums are bothersome, the early signs of periodontitis include receding gums and the formation of pockets between the gums and the teeth. Once the infection gets beneath your gum line, periodontitis can destroy tissues, ligaments, and bones in the mouth that ultimately can lead to tooth loss.
Signs of periodontitis include:
- Pain when chewing
- Poor tooth alignment
- Receding gums
- Pockets between the teeth and gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Sores on the inside of the mouth
- Loose or sensitive teeth
Periodontitis Treatment
When gingivitis progresses to periodontitis, treatment becomes much more complicated. Only your dentist and hygienist can perform periodontal treatment, which involves special dental procedures, and can require oral surgery. If your dentist determines that you have periodontitis, the treatment will depend on the severity of the infection. Some options include:
- Tooth Scaling and Root Planing: During this two-step procedure to treat periodontitis, your dental professional will scrape off the tartar that has built up on teeth both above and below the gum line (tooth scaling). Next, your dental professional will smooth rough spots on the tooth roots, making it more difficult for bacteria to collect and cause more plaque and tartar buildup.
- Flap Surgery: If the gum inflammation and pockets next to the teeth persist after a deep tooth-cleaning procedure, your dentist may recommend flap surgery. Flap surgery is a common dental procedure to treat periodontitis that is performed by a specialist called a periodontist. During flap surgery, the tartar is removed from the pockets that have formed alongside the teeth. The pockets are then closed with stitches, so the gum tissue once again hugs the teeth. Reducing the pockets makes it easier and more comfortable to brush and floss your teeth.
- Grafts: In severe cases of periodontitis in which bone and tissue have been destroyed, you may need bone or tissue grafts to replace the infected tissue. Your graft may involve a technique called guided tissue regeneration, in which a small piece of mesh is placed between the jaw bone and gums to allow both bone and tissue to re-grow. Guided tissue regeneration helps keep the gum tissue from expanding into the area where the bone should be, so both bone and tissue grafts have room to grow.
- Doxycycline Gel: Gel that contains doxycycline (an antibiotic) provides periodontal disease treatment by killing bacteria and shrinking the pockets that periodontal disease can cause along the gum line. Your periodontist applies the gel to the pockets after a tooth scaling/root planing procedure, and the antibiotic is released gradually over a period of about a week.
- Chlorhexidine Chip: Another periodontal disease treatment involves placing a small, antimicrobial gelatin chip in a tissue pocket along the gum line after tooth scaling/root planing, and the antimicrobial is released gradually over time.
- Minocycline Microspheres: For this type of periodontal disease treatment, the periodontist places tiny particles containing minocycline as an antibiotic in the tissue pockets after a tooth scaling/root planing procedure.
- Doxycycline Pill: Your periodontist may prescribe an antibiotic pill for periodontal disease treatment in addition to tooth scaling and root planing. A low-dose doxycycline pill can help prevent overactive enzymes from breaking down gum tissue after periodontal disease treatment.
Prevent Periodontitis: Stop Gingivitis Before It Starts
Prevention is the best way to avoid the need for painful, costly, and time-consuming periodontal treatment. By focusing on preventive health and oral hygiene through the use of an effective oral hygiene regimen, you can keep your gums and teeth healthy. To help prevent and reverse gingivitis, an early form of periodontal disease, try a Crest Pro-Health regimen. A Crest Pro-Health Advanced regimen helps protect your teeth and gums. This Crest Pro-Health Advanced regimen includes:
- Toothpaste: Toothpaste like Crest Gum Detoxify Deep Clean can play a key role in at-home treatment of gingivitis, an early form of periodontal disease, by preventing issues before they start. Crest Gum Detoxify can neutralize the bacteria found in plaque that builds up around the gum line. By using this as your daily toothpaste, it can help reverse early signs of gum disease and give you clinically proven healthier gums.
- Mouthwash: Crest Pro-Health Multi-Protection Mouthwash helps reduce gingivitis, an early form of periodontal disease by killing germs. Crest Pro-Health Multi-Protection Mouthwash provides 24-hour protection against gingivitis and plaque when used twice a day and it freshens your breath without the burning sensation of alcohol.
- Brush: To round out the Crest Pro-Health Advanced Regimen, choose a soft-bristled toothbrush that fits your mouth, such as the Oral-B Cross-Action Pro-Health Toothbrush, which features soft gum stimulators and a tongue cleaner.
- Floss: Twice-daily flossing is an important part of any oral care regimen. If your teeth and gums are sensitive, try Oral-B Glide Pro-Health Comfort Plus Floss.
When combined, these products work hard to keep your teeth and gums in good health. For effective gingivitis protection, in addition to noticeable whitening benefits,* you may also want to consider the breakthrough daily 2-step system, Crest Gum Detoxify + Whitening. And as always, don't forget to see your dentist for continued gingivitis prevention, an early form of periodontal disease. Be sure to see a dentist regularly for a professional cleaning and checkup. Your dentist can help you avoid periodontal disease by cleaning and examining your teeth to identify any minor problems before they become serious.
*At 3 weeks of treatment.
Discover More
 Inflamed Gums: Causes & Treatments for Gum Swelling
Inflamed Gums: Causes & Treatments for Gum Swelling






